In this blog, I will walk you through the Concepts of the TCP/IP Model in detail let us start with what is TCP/IP model👍
What is TCP/IP Model?
The TCP/IP model refers to the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol Model. This model is a part of the network domain designed specifically for organizing efficient and transmission of data.
This is a four-layered architecture model, where each layer implicit the required network protocols on the data to be transmitted, which remodels the data to the most optimum structure for efficient transmission over the network.
Features of the TCP/IP Model
Here are some interesting features of the TCP/IP model that stand out in the network concepts:
The TCP/IP model is among one of the most important network concepts that contributed to the working of ARPANET(you can refer to my last blog to know about ARPANET).
The TCP/IP model comprises four layers: the network access layer, internet layer, transport layer, and application layer.
The network model is implemented during network and communication-related issues.
Communication between different modes of network devices is possible through the application of various layers.
The layers in the model provide maintenance of communication channels, flow control, and reliability check format, among other applications in the form of protocols.
Layers of the TCP/IP Model
The TCP/IP model is divided into four different layers:
- Application layer
- Transport layer
- Internet layer
- Network Access layer
Each layer performs a specific task on the data that is being transmitted over the network channel, and data moves from one layer to another in a preset pattern as mentioned below:
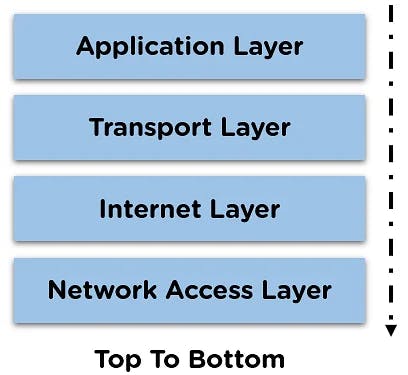
The above model represents the flow of data when it is being transmitted from the sender side. In the case of data being received, the layers of the model work in reverse order.
Now come, Let's take a look at each of the layers in detail:
Application Layer
This is the topmost layer which indicates the applications and programs that utilize the TCP/IP model for communicating with the user through applications and various tasks performed by the layer, including data representation for the applications executed by the user and forwards it to the transport layer.
The application layer maintains a smooth connection between the application and user for data exchange and offers various features such as remote handling of the system, e-mail services, etc.
Some of the protocols used in this layer are:
- HTTP: Hypertext transfer protocol is used for accessing the information available on the internet.
- SMTP: Simple mail transfer protocol, assigned the task of handling e-mail-related steps and issues.
- FTP: This is the standard protocol that oversees the transfer of files over the network channel.
Now, move on to the next layer,
Transport Layer
This layer is responsible for establishing the connection between the sender and the receiver device and also performs the task of dividing the data from the application layer into packets, which are then used to create sequences.
It also performs the task of maintaining the data, i.e., to be transmitted without error, and controls the data flow rate over the communication channel for smooth transmission of data.
The protocols used in this layer are:
- TCP: Transmission Control Protocol is responsible for proper transmission of segments over the communication channel. It also establishes a network connection between the source and destination system.
- UDP: User Datagram Protocol is responsible for identifying errors, and other tasks during the transmission of information. UDP maintains various fields for data transmission such as:
- Source Port Address: This port is responsible for designing the application that makes up the message to be transmitted.
- Destination Port Address: This port receives the message sent from the sender side.
- Total Length: The total number of bytes of the user datagram.
- Checksum: Used for error detection of the message at the destination side. Moving on to the next layer, you have -
Internet Layer
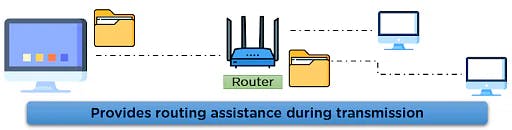
The Internet layer performs the task of controlling the transmission of the data over the network modes and enacts protocols related to the various steps related to the transmission of data over the channel, which is in the form of packets sent by the previous layer.
This layer performs many important functions in the TCP/IP model, some of which are:
It is responsible for specifying the path that the data packets will use for transmission. This layer is responsible for providing IP addresses to the system for the identification matters over the network channel. Some of the protocols applied in this layer are:
- IP: This protocol assigns your device a unique address; the IP address is also responsible for routing the data over the communication channel.
- ARP: This protocol refers to the Address Resolution Protocol that is responsible for finding the physical address using the IP address.
The last layer in the network model is the network access layer.
Network Access Layer
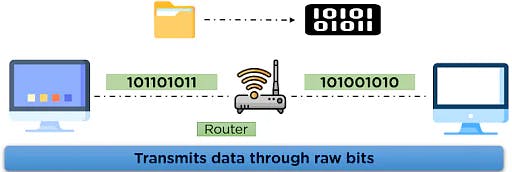
This layer is the combination of data-link and physical layer, where it is responsible for maintaining the task of sending and receiving data in raw bits, i.e., in binary format over the physical communication modes in the network channel.
It uses the physical address of the system for mapping the path of transmission over the network channel. Till this point in this tutorial on what is TCP/IP model, you understood the basic idea behind the model and details about its layers, now compare the model with another network model
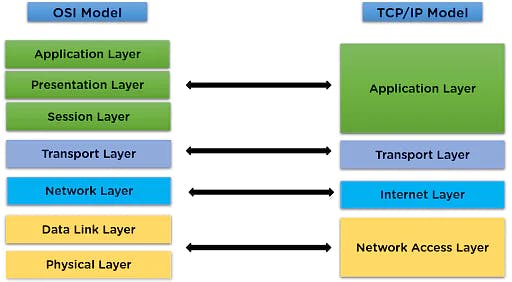
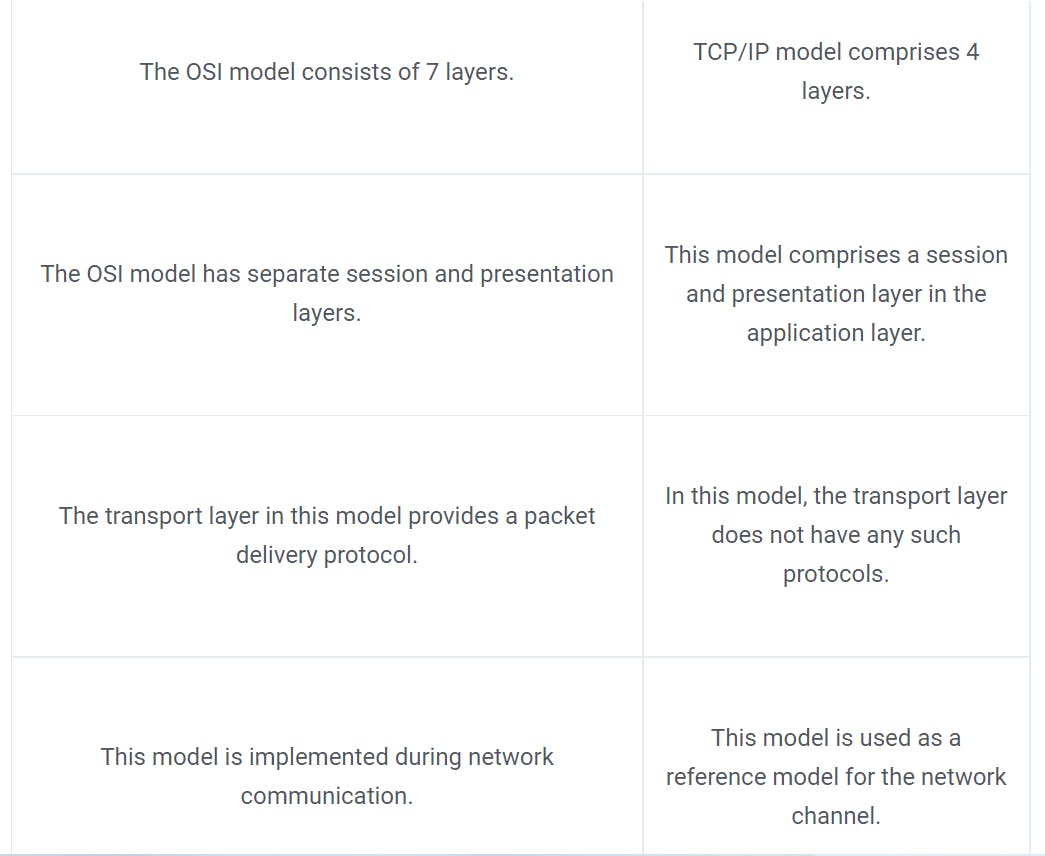
OSI Model vs. TCP IP Model
The TCP/IP model was designed in the 1960s to maintain and explain the transmission of data, whereas the OSI model is a network concept specifically for explaining the communication and working of data and protocols during the transmission of information.
Difference between OSI & TCP/IP Model

This is all about TCP/IP Model, Hope you enjoyed this Blog🧾 If have any doubts let me know in the comment section Hashnode🙂.
if you want to check out my content Follow me on Twitter and Linkedin as well🚀.
#BlogWithCC
